Introduction
What is Apache AirFlow?
Apache Airflow® is a platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows.
DAG
A Directed Acyclic Graph is a non-cyclic directional graph that describes all the data processing steps in a process
Workflows are usually defined with the help of Directed Periodic Graphs (DAGs)
Each DAG is defined in a DAG file, which defines a data processing, represented as a non-cyclic directional graph, where nodes are tasks and edges are dependencies between tasks.
Tasks in a DAG are typically processed sequentially or in parallel on a predetermined schedule
When a DAG is executed, it is called a DAG run
Task
- A task is a basic unit for performing a small task in the data processing. Each Task is a step in the process and can be scheduled to execute according to specific conditions.
Operator
- Each operator represents a specific task in the process, such as reading data from one data source, processing data, or writing data to another data source.
Sensor
- A sensor is a type of operator that is used to monitor events and conditions, and take corresponding actions.
- Sensors are often used to wait until a certain condition occurs before proceeding with the process.
How Airflow Works
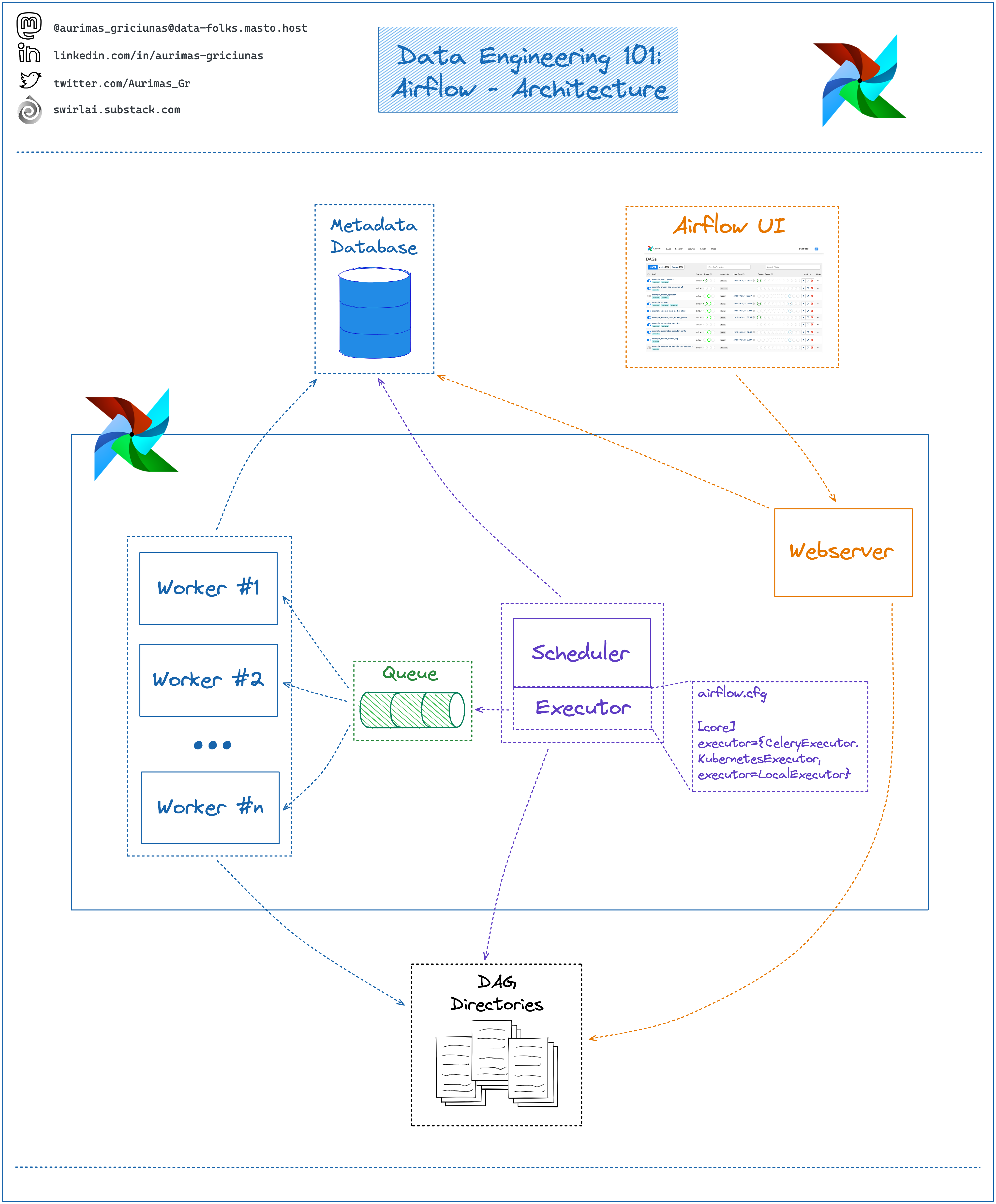
Drawing on an overview of the basic components of Apache Airflow.
- Scheduler: monitors all DAGs and their associated tasks. For a task, when the dependencies are met, the Scheduler will initialize the task. It checks active tasks to start periodically
- Executor: handles running these tasks by giving them to the worker to run
- Web server: Airflow’s user interface, which displays the status of tasks and allows users to interact with databases as well as read updated files from remote storage such as Google Cloud Storage, S3, etc.
- DAG Directory: a directory that contains the DAG files of data pipelines in Airflow.
- Metabase Database: used by Scheduler, Executor, and Web Server to store important information of each DAG, e.g. versions, statistics per run, scheduling interval, etc.
Amazon Web Services Connection
The Amazon Web Services connection type enables the AWS Integrations.
The Amazon Web Services Connection can be tested in the UI/API or by calling test_connection(), it is important to correctly interpret the result of this test. During this test components of Amazon Provider invoke AWS Security Token Service API GetCallerIdentity. This service can only check if your credentials are valid. Unfortunately it is not possible to validate if credentials have access to specific AWS service or not. If you use the Amazon Provider to communicate with AWS API compatible services (MinIO, LocalStack, etc.) test connection failure doesn’t mean that your connection has wrong credentials. Many compatible services provide only a limited number of AWS API services, and most of them do not implement the AWS STS GetCallerIdentity method.
Authenticating to AWS
Authentication may be performed using any of the options described in Boto3 Guide Credentials. Alternatively, one can pass credentials in as a Connection initialisation parameter.
To use IAM instance profile, create an “empty” connection (i.e. one with no AWS Access Key ID or AWS Secret Access Key specified, or aws://)